A new oral antibiotic for the treatment of gonorrhoea
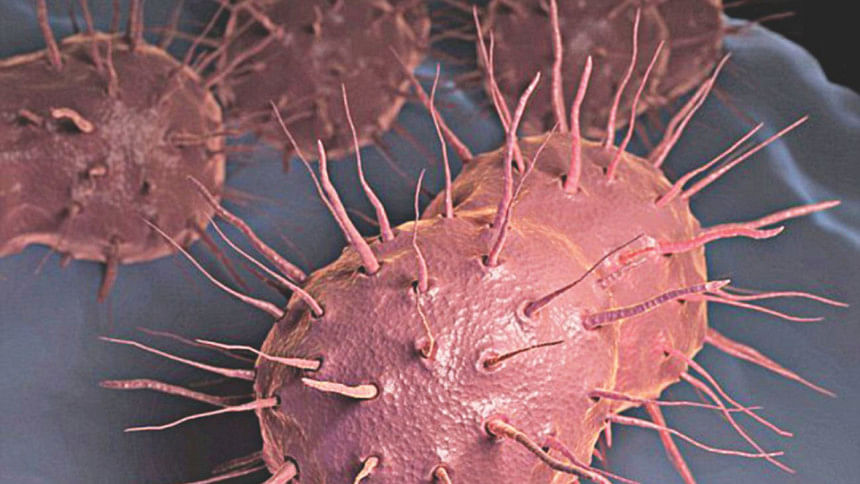
Zoliflodacin is a promising investigational oral antibiotic for the treatment of urogenital gonorrhoea.
The increasing prevalence of antimicrobial-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae has led to changes in treatment guidelines. Currently ceftriaxone, an injectable agent, plus azithromycin is the recommended therapy. Isolates resistant to both drugs have been reported, raising the specter of untreatable gonorrhoea in the future. Zoliflodacin (ETX0914), a first-in-class, investigational DNA gyrase/topoisomerase inhibitor, has received FDA "fast-track" designation for its development for oral treatment of gonorrhoea. A phase II, open-label, partially manufacturer-supported trial comparing a single dose of 2 or 3 gm of zoliflodacin with 500 mg of intramuscular ceftriaxone (randomized 7:7:4) for the treatment of gonorrhoea was conducted at five sites in the USA.
Approximately one third of participants had an adverse event. The most common adverse events with zoliflodacin were self-limited gastrointestinal events.

 For all latest news, follow The Daily Star's Google News channel.
For all latest news, follow The Daily Star's Google News channel. 



Comments