Pregnant women at greater risk for Hepatitis E
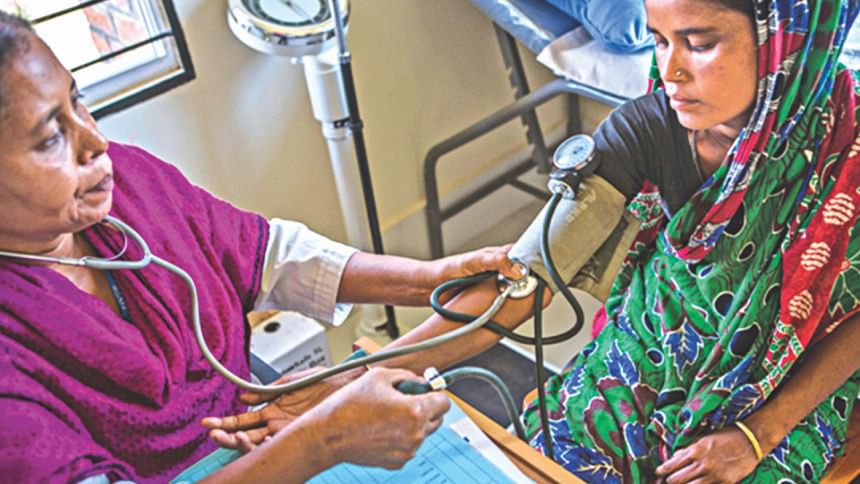
Researchers from the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health have found a link between pre-existing nutritional deficits and immune dysfunction and the risk of hepatitis E infection during pregnancy.
Hepatitis E, a virus that is largely transmitted through contaminated drinking water, can be particularly deadly in pregnant women. As many as 30% of pregnant women who contract hepatitis E die from the infection compared with an overall mortality rate of between 0.5-2%. Hepatitis E is likely responsible for as many as 10% of maternal deaths in South East Asia.
The study, published on January 6 in the journal American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, is thought to be the first to identify pre-existing characteristics that lead to an increased risk of hepatitis E infection.
"For decades, we've been asking why pregnant women who get hepatitis E die at an alarming rate. This research suggests that pre-existing differences could be the key we've been seeking," says study leader Alain Labrique, PhD, an Associate Professor in the Bloomberg School's Department of International Health.
"Even though women are exposed to similar environmental risk factors, the differences in pre-existing characteristics seem to put some women at a much higher risk of getting infected, sick and dying. These findings could pave the road for stepped-up nutritional monitoring of pregnant women in this part of the world and lead to recommendations for nutritional supplements."
Researchers found that anemia occurred in nearly three times the number of women who became infected compared to those who didn't (27.5% versus 10%). 45% of infected women had a body mass index that categorised them as underweight compared to a quarter of the control group. Researchers also found that women who were vitamin-D deficient and who had lower levels of zinc were more likely to be infected than the control group of pregnant women at a similar risk level who did not become infected with the virus.
95% of the women who became infected were vitamin-D deficient in the first trimester compared to 82.5% of the control group. In the third trimester, 17.5% of women were zinc- deficient compared to only 2.5% of the control group.
The study, which was conducted at the Bloomberg School's flagship JiVitA Research Project in Bangladesh, also found that women who became infected had higher levels of both pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines, important to immune system functioning. This suggests that pre-existing immune dysfunction may also increase the risk of getting hepatitis E or other infectious diseases.
"Most of the current knowledge about how hepatitis E affects pregnant women comes from studies looking at women who are already infected," says Labrique. "This population-based study was able to look at the health status of pregnant women before they became infected. If we can better understand what predisposes pregnant women to infection we could also develop better programs that prevent infection from ever occurring."

 For all latest news, follow The Daily Star's Google News channel.
For all latest news, follow The Daily Star's Google News channel. 







Comments