How To Avoid Catching The Ebola Virus
How is Ebola spread?
The Ebola virus is transmitted in the bodily fluids of people who are seriously ill, who are likely to be vomiting, bleeding or have diarrhoea. Blood, faeces and vomit are the most infectious fluids, and in late stages of the disease even tiny amounts can carry high loads of virus. But a nurse who got a patient's blood on their hands could wash it off with soap and water without any ill-effects. He or she would become ill only if they had a cut or abrasion on their hand or touched their mouth, eyes or nose, which would allow the virus to pass into their bodily fluids.
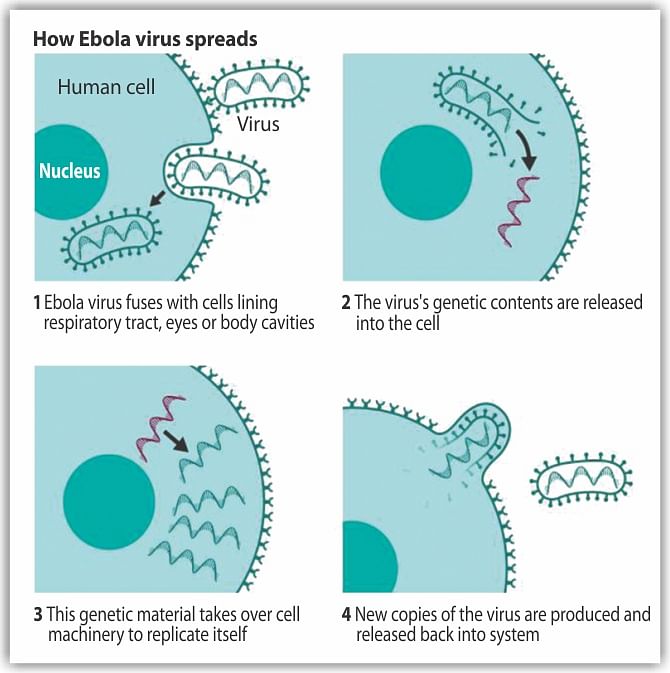
What about sweat – for example could I get Ebola from using gym equipment?
No. Nobody who had Ebola and was symptomatic, with intense muscle weakness and a fever in the early stages, would be well enough to go to the gym – and until they are symptomatic, they are not infectious. Sweat, anyway, is probably not a source of large amounts of virus – in fact, the World Health Organisation (WHO) says whole live virus has never been isolated from sweat.
How about saliva?
WHO says saliva at the most severe stage of the disease, and also tears, may carry some risk, but the studies are inconclusive. The virus has been detected in breast milk. A 2007 study in the Journal of Infectious Diseases is probably the most informative on where the virus hides.
Can I get Ebola from a toilet seat?
Yes – faeces from somebody with Ebola are a real hazard and the virus has also been detected in urine. But there would only be a danger if a seriously sick person had used the toilet and contaminated it and that is most likely in their home or hospital. Public toilets, in general, are very unlikely to be a risk.
Can it be sexually transmitted?
Yes, and the virus lasts in the semen of people who have recovered, maybe for as long as 90 days.
Could I catch Ebola from using a taxi that has taken a patient to hospital?
The virus can be transmitted on surfaces that bodily fluids have touched, so if somebody had bled or vomited on the seat, there would be a risk to anybody who had a cut or touched their face with contaminated hands. In Europe or the US, if a patient was diagnosed with Ebola, there would be a massive effort from the public health authorities to trace their movements as well as their contacts. Any taxi they had travelled in while sick would have to be decontaminated.
Could I catch Ebola from door handles a patient had touched?
Yes, if the handle was contaminated with blood, vomit or faeces, which would be more likely in the house where the patient had been living when they fell sick, or in the hospital. But if people have intact skin, do not touch their eyes, nose or mouth and frequently wash their hands, they will not get infected.
How long can the virus survive?
The virus is quite fragile and is easily destroyed by UV light, drying out, high temperatures (which is helpful in west Africa) and disinfectants including soapy water and alcohol gel. The longest it is likely to survive is a few days, if left in a pool of bodily fluid in a cool, damp place.
Is food safe?
Yes, if it is cooked. The Ebola virus is inactivated through cooking. Raw bush meat is a risk. Past outbreaks of Ebola in Africa came from the hunting, butchering and preparing of bush meat for people to eat.
Is Ebola virus airborne? Should I wear a mask?
No. The virus is not airborne. In spite of speculation, the UN Ebola Mission for Emergency Response says extensive studies of the virus have not shown any airborne transmission. Patients do not cough and sneeze a lot with this disease and the WHO states in an advisory notice: “Epidemiological data emerging from the outbreak are not consistent with the pattern of spread seen with airborne viruses, like those that cause measles and chickenpox, or the airborne bacterium that causes tuberculosis.”
What if somebody coughs or sneezes in my face?
There is a theoretical possibility that a person heavily infected with Ebola could cough violently and send wet, heavy droplets into the face of somebody nearby. The person most at risk of catching Ebola this way would be whoever is nursing the patient, and they would hopefully be wearing protective clothing including a mask.
Source: guardian

 For all latest news, follow The Daily Star's Google News channel.
For all latest news, follow The Daily Star's Google News channel. 



Comments