Exploring alternative energy sources: The future of renewable power

El Nino, La Nina, wildfire, floods, heatwaves – all these terms have been plastered on every news source, both digital and print for the past few years. It seems that the detrimental effects of global climate change have dawned upon us, it is not a phenomenon that "may happen" in the distant future.
A significant part of the discourse and dialogue surrounding global warming and climate change centres on energy sources, particularly the near future exhaustion of conventional fuel sources and the emergence of renewable energy sources as a greener and cleaner alternative. Below, we discuss the future of renewable energy and the types of renewable fuels we have access to.
What is renewable energy?
Renewable energy is the energy derived from natural sources which are either virtually limitless in supply or replenish at a faster rate than that at which they are consumed. Examples include solar energy and wind energy. Our current sources of fuel and energy, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, are finite in quantity and will not be replenished in our lifetimes and many lifetimes after us.
The impact of non-renewable energy
Fossil fuels account for the lion's share of global energy sources. These carbon-based fossil fuels were formed under the earth about 300-360 million years in high heat and high-pressure environments from the remains of dead plants and animals. Since the industrial revolution, the exponential growth of human civilisation meant ever-increasing demands for energy and renewable sources simply cannot keep up. Moreover, such high-volume usage has irreversible implications for the environment, flora and fauna.
When fossil fuels are burned, they release large amounts of carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas, into the air. Greenhouse gases trap heat in our atmosphere, causing global warming. It also causes deadly air pollution.
Advantages of using renewable energy
Renewable energy emits significantly less carbon dioxide in the air. These sources will never be exhausted, for instance, the sun will never stop shining and the wind will keep blowing. Cleaner fuels cause little to no air pollution, which is both better for the environment and for our health.
Renewable energy will expand energy access in developing countries, particularly for non-grid-connected or remote, coastal, or islanded communities. It will diversify energy supply and create newer jobs in the economy. Moreover, thanks to research and modern technology, renewable energy has now become cheaper than fossil fuels.
Sources of renewable energy
Solar Energy
Solar energy is the most well-known source of renewable energy. The sun is the ultimate source of energy for all our energy sources and fuel. The sun provides the world with sustenance. The rate at which solar energy is intercepted by the Earth is about 10,000 times greater than the rate at which humankind consumes energy. The amount of solar energy that reaches the earth's surface in one hour is more than the planet's total energy requirements for a whole year.
Research and scale have plummeted the cost of solar energy, making it the cheapest form of electricity. Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity and these panels last for a good 30 years.
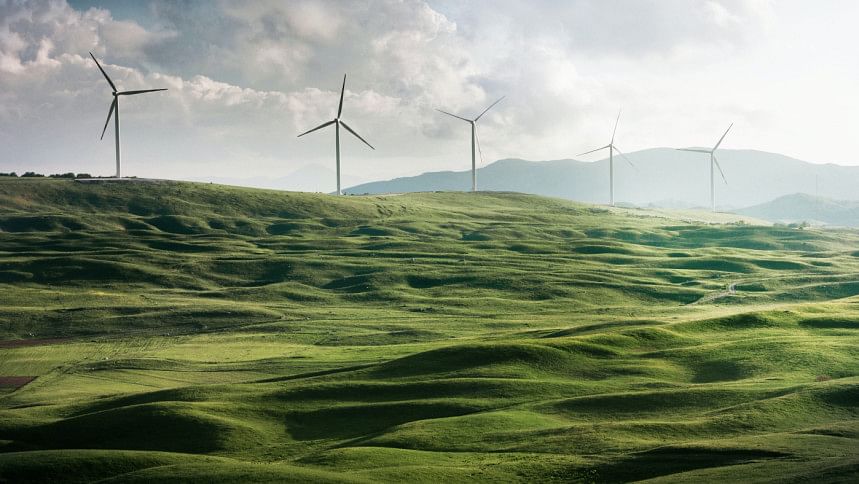
Wind energy
Wind energy has been used since ancient times to power activities in civilisation. 5,000 years ago, ancient Egyptians made boats powered by the wind. In 200 BCE, people used windmills to grind grain in the Middle East and pump water in China.
Turbines located on land (onshore) or sea or freshwater (offshore) are used to harness the energy from moving wind. The world's technical potential for wind energy exceeds global electricity production.
Hydroelectric power
Hydroelectric power uses the movement of water current from higher to lower elevations to produce electricity. Hydroelectric power plants are established on dams which control the water flow, creating a reservoir. The water contained in this artificial reservoir is spun on turbines to produce electricity.
The biggest advantage of hydroelectric power over wind and solar energy is that it is not dependent on the weather. Hence, it is a more dependable source of clean energy as engineers control the amount of water. However, these power plants don't work for a long time, as silts and dirt pile up. Moreover, these dams can be damaging to the environment as the artificial reservoirs can drown both human towns and underwater river habitats.
Geothermal energy
Geothermal energy is the utilization of the heat within the earth to produce electricity. The earth's centre is very hot, having a temperature of about 6,000°C. This heat is extracted from underground hot water reservoirs or by human-made reservoirs for direct heating and electricity generation.
While this source of energy is clean, it is scarce globally. Almost 90 per cent of residents in Iceland use geothermal energy to heat their houses.
Other sources of energy
Some other notable sources of energy include tidal energy, biomass energy, and some others. Tidal energy uses the tides in the ocean to generate electric energy while biomass makes use of the stored chemical energy from the sun. By converting agricultural, industrial and domestic waste into solid, liquid and gas fuel, biomass generates power at a much lower economic and environmental cost.

 For all latest news, follow The Daily Star's Google News channel.
For all latest news, follow The Daily Star's Google News channel. 







Comments