'New state of water molecule discovered'
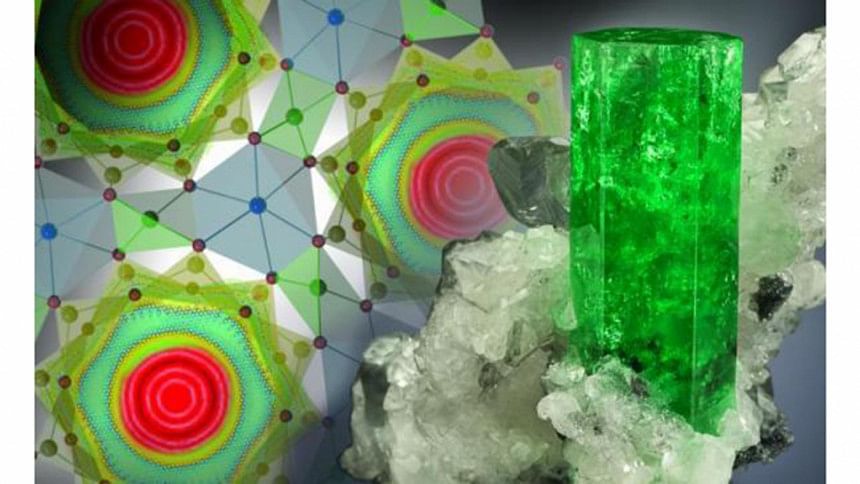
Water molecules have been observed behaving unlike gas, liquid or solid states by scientists at the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory, reports UPI.com.
According to UPI, researchers discovered the new state while subjecting water molecules to extreme confinement.
When water molecules were pushed into nanoscale tubes or channels in the mineral beryl, the water molecules become delocalized around a ring, with each molecule adopting "an unusual double top-like shape."
The new molecular state has been described by researchers in the journal Physical Review Letters.
"This means that the oxygen and hydrogen atoms of the water molecule are delocalized and therefore simultaneously present in all six symmetrically equivalent positions in the channel at the same time," lead study author Alexander Kolesnikov, of ORNL's Chemical and Engineering Materials Division, said in news release.
"It's one of those phenomena that only occur in quantum mechanics and has no parallel in our everyday experience."
This spreading of water molecules when confined was not just unexpected, it breaks the rules of classical physics. The behavior, known as "tunneling," describes a molecule passing through a barrier without the energy required to do so -- in other words, it defies physics, reports UPI.com.
"The average kinetic energy of the water protons directly obtained from the neutron experiment is a measure of their motion at almost absolute zero temperature and is about 30 percent less than it is in bulk liquid or solid water," Kolesnikov said.
"This is in complete disagreement with accepted models based on the energies of its vibrational modes."
Because the confinement measured at ORNL is comparable to the experience of water molecules trapped in rocks, soil and cell walls, the novel findings are expected to have real-world impact on the discussions happening within a variety of scientific disciplines -- cellular biology, geology and more.
Source: upi.com

 For all latest news, follow The Daily Star's Google News channel.
For all latest news, follow The Daily Star's Google News channel. 








Comments