Artificial intelligence improves wrist fracture detection
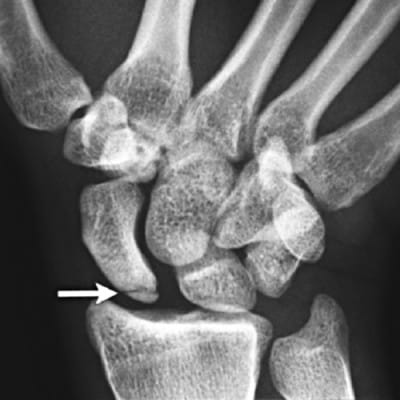
Missed fractures are a common category of diagnostic errors and can cause malunion, osteonecrosis, and arthritis, with consequent impairment of function. In a study, researchers examined 135,845 x-rays of various bones (nearly 35,000 of which involved the wrist). Senior orthopaedic surgeons scored each image for the presence of fractures and used neural network artificial intelligence (AI) techniques to 'train' a computer to diagnose wrist fractures.
Researchers then conducted a controlled experiment with 40 emergency department clinicians: Each participant was shown an x-ray and asked to determine the presence or absence of a fracture. Then, those in a randomly assigned 'aided' group were shown the computer model's fracture assessment and asked again to determine the presence or absence of a fracture. When aided performance versus unaided performance were compared in a series of 300 x-rays, sensitivity for diagnosing fracture was 92% versus 81%, and specificity was 94% versus 88%.

 For all latest news, follow The Daily Star's Google News channel.
For all latest news, follow The Daily Star's Google News channel. 



Comments