Antibiotics Awareness Week: How we can prevent resistance

World Antibiotics Awareness Week, which takes place November 12 to 18 and is managed by the World Health Organization, aims to increase global awareness of antibiotic resistance and prevent it spreading further. Here we round up some facts and figures on antibiotic resistance and why it is important we all play our role in fighting against it.
-- 33,000- the number of people killed in Europe in 2015 due to drug-resistant bacteria according to a study published in the journal The Lancet Infectious Diseases earlier this month.
-- 65 and over and those under 12 months- the ages with the highest mortality rate in 2015 due to drug-resistant bacteria.
-- 700,000- the number of deaths related to drug-resistant infections globally in 2016 according to a group of UK experts.
-- 65- the percentage increase in worldwide antibiotic use between 2000 and 2015, driven by users in low- and middle-income countries, mainly China, India, and Pakistan.
-- 200- the percentage increase in antibiotic use predicted to occur by 2030.
-- 2.4 million- the number of people across Europe, North America and Australia who could die from superbug infections by 2050 unless unnecessary antibiotic use is reduced, according to the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
-- 12- the number of classes of deadly bacteria, such as those that cause pneumonia or urinary tract infections, which are increasingly resistant to existing antibiotics and urgently in need of new treatments according to a recent report by the WHO.
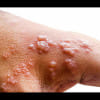
-- 33- the percentage of surgical patients who get a postoperative infection, of which 51 percent can be antibiotic resistant. Antibiotic resistance is threatening our ability to treat common infectious diseases and minor injuries, which could result in prolonged illness, disability and even death.
-- 51- the number of new drugs under development to treat infections according to a recent study by the WHO, although the agency says only eight add any value to current treatments.
-- 100- the percentage of the population who can be affected if we misuse antibiotics. Antibiotics resistance occurs everywhere in the world, and is leading to untreatable infections which can affect anyone, of any age, in any country. We can all play a role by taking care with antibiotics.
-- 0- the number of times you can take antibiotics to treat viral infections; you cannot take them to treat a cold or flu.
-- 0- the number of times you should share antibiotics. Only take antibiotics prescribed to you, and never share them, not even with family.

 For all latest news, follow The Daily Star's Google News channel.
For all latest news, follow The Daily Star's Google News channel. 






Comments