Conformal radiotherapy & medical physics
Cancer, a leading cause of death globally. Radiotherapy is essential in managing the cancer patient alongside chemotherapy or surgery for cure or palliation. About 60% of patients receive radiotherapy as definitive, adjuvant or palliative to surgery or chemotherapy each year. Radiotherapy aims to deliver a precise dose of radiation to the defined tumour volume without causing damage to the surrounding normal tissues.
However, medical physics applies concepts and methods of physics in medical science for diagnosis and treatment purposes. The newest development of radiation treatments is Three Dimensional Conformal Radiotherapy (3DCRT), Intensity Modulated Radiotherapy (IMRT), Image-Guided Radiotherapy (IGRT), Stereotactic Radio Surgery and Radiotherapy (SRS, SRT), Rapid Arc or Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy (VMAT).
A medical physicist usually completes a two-year Master's degree in Physics or a Bachelor of Medicine and Surgery. Oncologists rely on medical physicists for machine selection, acceptance testing, and radiation therapy quality control.
To control tumours rationally applying radiation at optimum dose, a radiotherapy team consisting of oncologists, radiologists, medical physicists, and medical technologists is required.
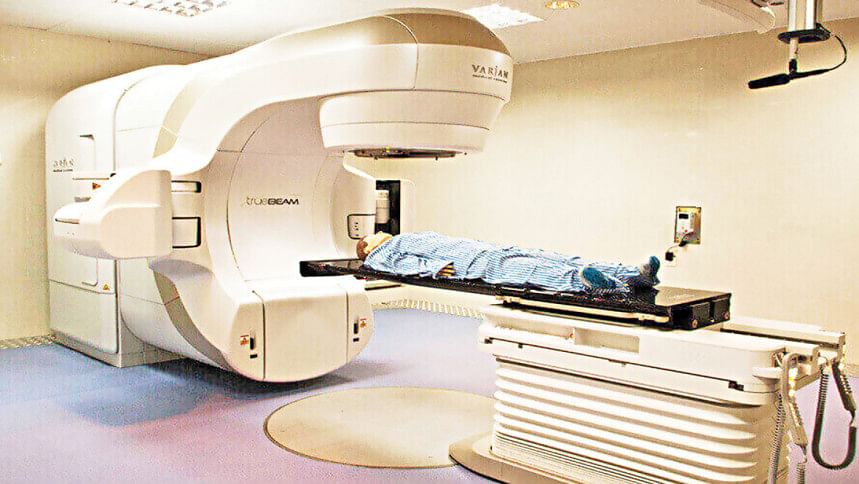
Conformal radiotherapy (3DCRT) is the advancement of radiation therapy where radiation is given to cancer areas with sparing the surrounding normal tissue by using a CT simulator, Multileaf Collimator (MLC), Treatment Planning System (TPS), & Linear Accelerator (LINAC) machine.
The first step is a CT scan of the patient with an immobilisation device and transporting the image to the Treatment Planning System (TPS), a new computer with upgraded software. Then, the radiation oncologist has to contour the target volume and Organ at Risk (OAR) correctly and meticulously. It is noted that accurate contouring leads to perfect planning and quality radiation treatment. Next, the medical physicist plans treatment after evaluating TPS data. The oncologist approved the best planning with less chance of normal tissue complication and sent all data to the Linear Accelerator (LINAC) machine. The medical technologist then treats accordingly. Bangladesh has all the treatment options.
There is a need for updated training for all the Radiotherapy team members to offer standard and quality radiotherapy.
The writer is the Head of the Department of Oncology, Delta Medical College and Hospital.
E-mail: [email protected]

 For all latest news, follow The Daily Star's Google News channel.
For all latest news, follow The Daily Star's Google News channel. 



Comments