Treatment facilities for brain tumours available locally
Brain tumours are the most typical type of solid tumours in children. Also, they affect many adults each year in our country. This disease can affect anyone at any age. So far, we don't know the cause for most brain tumours. This disease and its treatment may result in physical and emotional suffering for the affected and the family.
This whole experience of being diagnosed with a brain tumour and then undergoing the treatment is often challenging for the entire family.
Modern management can cure this tumour in some patients and relieve the suffering in most patients.
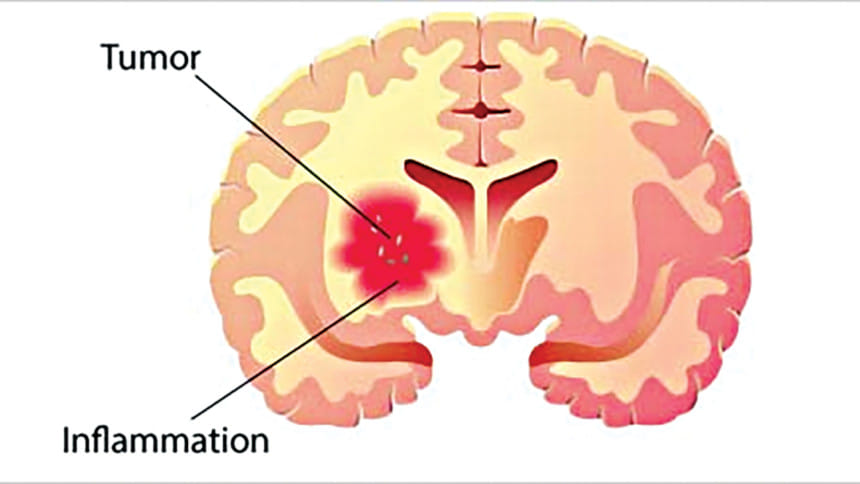
A mass of abnormal tissue growing in any part of the brain is called a brain tumour. For some unknown reason, some brain cells multiply in an uncontrolled manner. These tumours can arise from any part of the brain, the spinal cord or the nerves.
Broadly these tumours can be divided into benign and malignant tumours. Benign tumours grow slowly and do not spread to other parts. But as they gradually increase in size, they can cause pressure on the normal brain and interfere with mental and body function.
Malignant tumours or cancers are aggressive tumours that grow fast and infiltrate the surrounding brain. Sometimes they spread to other parts of the brain or spine. With aggressive and timely treatment, some of these can be cured.
Brain tumours cause headaches with or without nausea and vomiting due to the tumour growth within the tight space inside the skull. It causes swelling in the surrounding brain and can cause block the free flow of cerebrospinal fluid. Thus it results in the dilatation of the ventricles - a condition called Hydrocephalous.
Seizures or epilepsy or fits can be caused by the treatment in certain parts of the brain. A seizure is a sudden jerky movement of one part of the body or a brief loss of consciousness lasting from a few seconds to a few minutes. Limb weakness and abnormal sensation can be a symptom of a tumour in certain part of the brain, especially in and around the motor or sensory cortex. Generally, the opposite side is affected, i.e. right-sided weakness by a tumour in the left motor cortex. Other symptoms are unsteady walking or imbalance; vision may be blurred or lost if the optic nerve is compressed. Recent or long term memory may become weak, speech problems, changed behaviour, lethargy, drowsiness and loss of consciousness are other symptoms of brain tumour.
Diagnosis can be made by detailed history, medical examinations, CT scan, MRI of Brain, angiogram, CSF test, hormone and blood test, EEG may be done.
Then the tumour tissue removed by surgery or biopsy is processed and stained with special chemical dyes and then carefully examined under the microscope.
Treatment modalities are 1. Surgery, 2. Radiotherapy, and 3. Chemotherapy. Radiotherapy plays a vital role in all malignancies to prevent or delay recurrence; stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) or stereotactic radiotherapy (SRT) is a specialised type of radiotherapy treatment. This treatment is used for some small tumours at a critical location to give high radiation doses precisely.
To achieve such high precision, a special head frame is fitted on the patient's skull. Then CT, MRI scan and computer planning is done. This treatment is sometimes given as a single treatment (stereotactic radiosurgery) or multiple treatments over many weeks.
Radiation complications are generally mild and manageable – hair fall, loss of appetite or tiredness may occur one to three months following radiotherapy. Many patients feel very lethargic and sleepy due to the radiation. This gradually improves within few months. Suppose a high dose of radiation is given to a large area. In that case, there is about a 5% risk of brain damage (necrosis) due to radiation itself.
Excellent news that all diagnostic and treatment facilities in our country are available. Standard and quality radiotherapy treatment for brain tumours are possible.
The writer is the Head of the Department of Oncology, Delta Medical College and Hospital, Bangladesh. E-mail: [email protected]

 For all latest news, follow The Daily Star's Google News channel.
For all latest news, follow The Daily Star's Google News channel. 



Comments