Diabetes caused 1.5 million fatalities worldwide
Diabetes is a long-term illness characterised by inadequate insulin synthesis or poor insulin administration. Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. Hyperglycaemia, or high blood sugar, is caused by uncontrolled diabetes, and it damages a variety of body systems, including neurons and blood vessels.
Type 2 diabetes, which primarily affects adults and arises when the body develops insulin resistance or does not produce enough, is the most prevalent. During the previous three decades, type 2 diabetes has become far more prevalent in countries of all income levels.
Type 1 diabetes, also known as juvenile diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetes, is a long-term condition in which the pancreas produces little or no insulin on its own. In 2014, 8.5% of individuals aged over 18 years had diabetes. Unfortunately, in 2019, diabetes caused 1.5 million fatalities worldwide, with 48% occurring before 70 . Therefore, proper interventions and strategies are imperative to curb the occurrence of such progressive metabolic disease.
World Diabetes Day is observed on November 14th to raise public awareness among the public regarding the disease. This year the theme for World Diabetes Day is "Access to diabetes care". Diabetes care is unavailable to millions of individuals throughout the world. Yet, to control their illness and minimise complications, people with diabetes need constant care and assistance. Besides, World Diabetes Day is an opportunity to rebuild awareness of diabetes as a worldwide public health concern and what can be done, both collectively and individually, to improve diabetes prevention, diagnosis, and management.
The World Health Organisation (WHO) and partners have taken advantage of the 100th anniversary of the discovery of insulin to highlight the enormous disparity between those who need insulin to control their diabetes and those who have access to essential technologies such as blood glucose meters and test strips. The campaign's symbol is a blue circle established in 2007 when the United Nations passed a resolution on diabetes. The blue circle represents diabetes awareness throughout the world. It represents the diabetic community's worldwide solidarity amid the diabetic epidemic.
The following are essential components of diabetic care:
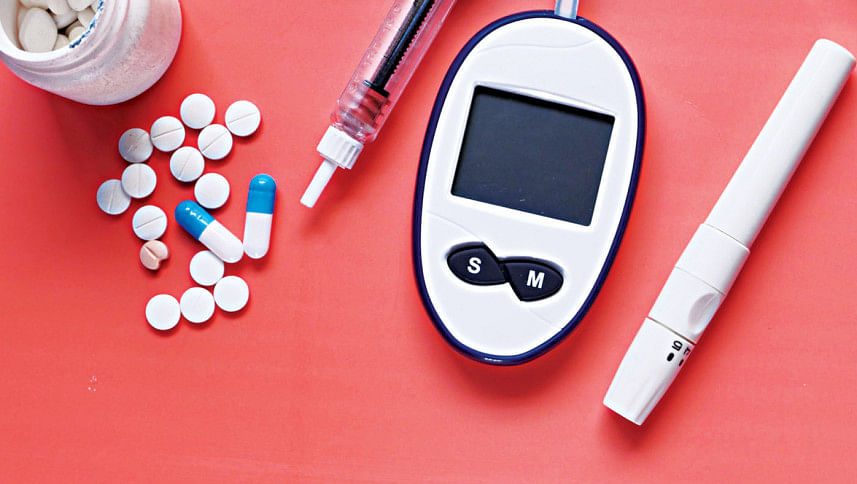
• Access to insulin: Unfortunately, millions of diabetes patients cannot obtain the insulin they require, although insulin was discovered 100 years ago.
• Access to oral medications: To cure their disease, many patients need to take oral drugs. Unfortunately, they are still inaccessible or prohibitively expensive in many low- and middle-income countries.
• Access to self-monitoring: The monitoring of blood glucose levels is an essential aspect of diabetes management. Many patients are unable to get the required supplies and equipment.
• Access to education and psychological support: Diabetes patients need ongoing education and psychological support to manage their condition. However, many persons with diabetes, paradoxically, do not have access to diabetes education.
• Access to healthy food and a safe place to exercise: People with diabetes, or those at risk of getting it, need to consume nutritious foods and exercise in a secure setting. Both are essential aspects of diabetes treatment and prevention.
An early diagnosis is a foundation for living well with diabetes; the longer a person goes without being recognised and treated for diabetes, the worse their health outcomes are. Basic diagnostics, such as blood glucose tests should be easily accessible in primary care settings. Patients should require specialised evaluation or treatment for complications regularly.
E-mail: [email protected]

 For all latest news, follow The Daily Star's Google News channel.
For all latest news, follow The Daily Star's Google News channel. 



Comments