Understanding and treating hyperpigmentation
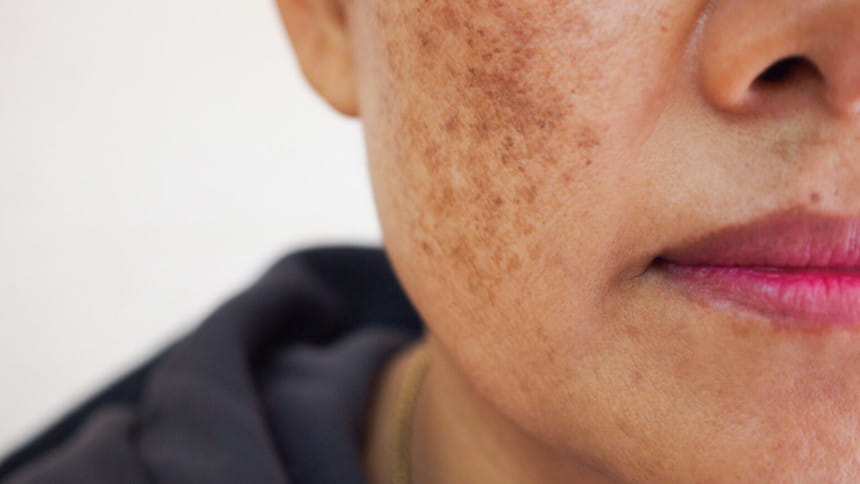
Hyperpigmentation is a common skin concern characterised by dark patches caused by excess pigment within the skin due to increased melanin production. Melanin, responsible for skin colour, can become irregularly dispersed, leading to hyperpigmentation. Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) often occurs after skin injury or inflammation, particularly in darker skin tones, lasting longer and being more severe. Melasma, another common cause, manifests as tan patches on sun-exposed areas of the face, often linked to hormonal changes and sun exposure. Photoaging, resulting from cumulative sunlight exposure, presents as sun spots or lentigines on chronically sun-damaged skin.
Treating hyperpigmentation requires patience and sun protection. Sunscreen with SPF 30+ is essential to prevent exacerbations from UV exposure. While many hyperpigmentation types resolve over time, fading can take months or years. Topical treatments like hydroquinone, retinoids, and vitamin C, along with procedures such as chemical peels and laser therapy, aid in resolution. Treatment efficacy varies based on the underlying cause, and prescription-strength management may be necessary in some cases. Consulting a skincare expert helps determine the most suitable treatment approach and ensures safe and effective management.

 For all latest news, follow The Daily Star's Google News channel.
For all latest news, follow The Daily Star's Google News channel. 



Comments