The Journey of Islamic Banking in Bangladesh
The journey of Islamic banking began with the goal of conducting banking business in Muslim countries around the world in accordance with Islamic Shariah.
The initial effort to establish an Islamic financial institution took place in Pakistan in the late 1950s with the establishment of a local Islamic bank in a rural area. However, the initiative did not yield fruitful results.
Later, the second experiment with Islamic banking was conducted in Egypt between 1963 and 1967 through the establishment of the Mit Ghamr Savings Bank in a rural area of the Nile Delta. The bank's operations were based on the Islamic principles of not charging interest to depositors or borrowers.
Subsequently, Al-Rajhi Banking Investment Corporation started its operations in 1985 and established active relationships with major manufacturing and trading companies in Europe, as well as several US corporations.
The success of Al-Rajhi in operating profitably in various parts of the world motivated the Saudi government to fully embrace Islamic banking.
In 1975, the Muslim countries founded the Islamic Development Bank (IDB) as a multinational corporation to support social and economic development in Muslim nations within an Islamic framework, and Bangladesh became member of the organization.
The establishment of the IDB facilitated the journey of Islamic banking in the Bangladesh. Several local individuals, as well as the Islamic Development Bank (IDB) and various financial institutions, began extending their cooperation to establish Islamic banks in the country.
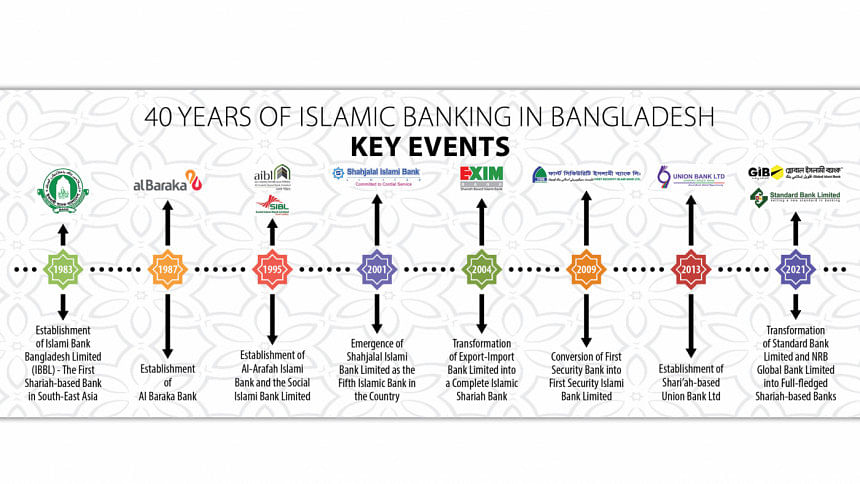
As part of the journey, the launch of the Islamic bank in Bangladesh began in 1983 with the establishment of Islami Bank Bangladesh Limited (IBBL).
Along the path of success of the country's first Islamic bank, several other Islamic banks were established in subsequent years. Al Baraka Bank was established in 1987, Al-Arafah Islami Bank in 1995, and the Social Investment Bank (Currently known as Social Islami Bank Limited ) was also established in the same year.
As the fifth Islamic bank in the country, Shahjalal Islami Bank Limited emerged as a scheduled bank in 2001.
Meanwhile, two traditional banks, Export-Import Bank Limited and the First Security Bank, have transformed into complete Islamic Shari'ah Banks. Exim Bank commenced banking operations in 1996 and started its new journey as an Islamic bank in July 2004, while First Security Bank made the transition in January 2009.
Subsequently, the Shari'ah-based 'Union Bank' was established in 2013, and Standard Bank Limited and Global Islami Bank Limited underwent transformations to become Shari'ah-compliant banks.
Currently, a total of 10 full-fledged Islamic banks are operating in Bangladesh, with 1,659 branches, while the entire banking system had a total of 11,153 branches as of December 2022, according to the Bangladesh Bank.
Additionally, 23 Islamic banking branches of 11 conventional commercial banks and 535 Islamic banking windows of 13 conventional commercial banks are also providing Islamic financial services in Bangladesh.
The total employment in the Islamic banks stood at 49,851 as of December 2022.
Contribution to the economy
"Islamic finance has emerged as an effective tool for financing economic activities worldwide. Islamic banks in Bangladesh have made a significant contribution to the country's economy," said Shah Md Ahsan Habib, a professor at the Bangladesh Institute of Bank Management (BIBM).
He further added, "Now, Islamic banking is a well-established component of the banking industry, accounting for approximately one-third of the total market share."
Professor Habib emphasized that Islamic financial institutions are playing a crucial role in supporting agricultural finance, contributing to improved food security, promoting financial sector development, and enhancing financial inclusion.
When contacted, Mohammed Monirul Moula, the managing director of IBBL, said that the Shariah-based banking system has been comprehensively contributing to ensuring general well-being, equity, and justice. It aims to promote better provisioning and reduce the gap between the rich and the poor.
"During the 40 years' journey of Islamic Banking in Bangladesh, it has achieved a galloping market share," he said.
Moula further stated that the market share of Shariah-based banking is as follows: 26 percent in deposits, 26 percent in imports, 24 percent in exports, 39 percent in remittances, 27 percent in industrial finance, 17 percent in agriculture investment, and 38 percent in CMSME (Cottage, Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises) investment.
Islamic banking has generated employment opportunities for approximately 1.20 crore people. IBBL alone has contributed $12 billion to the country's reserves since its inception, he added.
Moula also mentioned that Shariah-based banking holds a 50 percent market share of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) in the banking sector, with IBBL alone contributing around 29 percent.

 For all latest news, follow The Daily Star's Google News channel.
For all latest news, follow The Daily Star's Google News channel. 





Comments